NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION BY JOINTLY LEARNING TO ALIGN AND TRANSLATE
Papers and Code
AligNART: Non-autoregressive Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Estimate Alignment and Translate
Sep 14, 2021



Non-autoregressive neural machine translation (NART) models suffer from the multi-modality problem which causes translation inconsistency such as token repetition. Most recent approaches have attempted to solve this problem by implicitly modeling dependencies between outputs. In this paper, we introduce AligNART, which leverages full alignment information to explicitly reduce the modality of the target distribution. AligNART divides the machine translation task into $(i)$ alignment estimation and $(ii)$ translation with aligned decoder inputs, guiding the decoder to focus on simplified one-to-one translation. To alleviate the alignment estimation problem, we further propose a novel alignment decomposition method. Our experiments show that AligNART outperforms previous non-iterative NART models that focus on explicit modality reduction on WMT14 En$\leftrightarrow$De and WMT16 Ro$\rightarrow$En. Furthermore, AligNART achieves BLEU scores comparable to those of the state-of-the-art connectionist temporal classification based models on WMT14 En$\leftrightarrow$De. We also observe that AligNART effectively addresses the token repetition problem even without sequence-level knowledge distillation.
Accurate Word Alignment Induction from Neural Machine Translation
Apr 30, 2020



Despite its original goal to jointly learn to align and translate, prior researches suggest that the state-of-the-art neural machine translation model Transformer captures poor word alignment through its attention mechanism. In this paper, we show that attention weights do capture accurate word alignment, which could only be revealed if we choose the correct decoding step and layer to induce word alignment. We propose to induce alignment with the to-be-aligned target token as the decoder input and present two simple but effective interpretation methods for word alignment induction, either through the attention weights or the leave-one-out measures. In contrast to previous studies, we find that attention weights capture better word alignment than the leave-one-out measures under our setting. Using the proposed method with attention weights, we greatly improve over fast-align on word alignment induction. Finally, we present a multi-task learning framework to train the Transformer model and show that by incorporating GIZA++ alignments into our multi-task training, we can induce significantly better alignments than GIZA++.
Generalised Unsupervised Domain Adaptation of Neural Machine Translation with Cross-Lingual Data Selection
Sep 09, 2021



This paper considers the unsupervised domain adaptation problem for neural machine translation (NMT), where we assume the access to only monolingual text in either the source or target language in the new domain. We propose a cross-lingual data selection method to extract in-domain sentences in the missing language side from a large generic monolingual corpus. Our proposed method trains an adaptive layer on top of multilingual BERT by contrastive learning to align the representation between the source and target language. This then enables the transferability of the domain classifier between the languages in a zero-shot manner. Once the in-domain data is detected by the classifier, the NMT model is then adapted to the new domain by jointly learning translation and domain discrimination tasks. We evaluate our cross-lingual data selection method on NMT across five diverse domains in three language pairs, as well as a real-world scenario of translation for COVID-19. The results show that our proposed method outperforms other selection baselines up to +1.5 BLEU score.
Saliency-driven Word Alignment Interpretation for Neural Machine Translation
Jun 27, 2019



Despite their original goal to jointly learn to align and translate, Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models, especially Transformer, are often perceived as not learning interpretable word alignments. In this paper, we show that NMT models do learn interpretable word alignments, which could only be revealed with proper interpretation methods. We propose a series of such methods that are model-agnostic, are able to be applied either offline or online, and do not require parameter update or architectural change. We show that under the force decoding setup, the alignments induced by our interpretation method are of better quality than fast-align for some systems, and when performing free decoding, they agree well with the alignments induced by automatic alignment tools.
Controlling Utterance Length in NMT-based Word Segmentation with Attention
Oct 18, 2019


One of the basic tasks of computational language documentation (CLD) is to identify word boundaries in an unsegmented phonemic stream. While several unsupervised monolingual word segmentation algorithms exist in the literature, they are challenged in real-world CLD settings by the small amount of available data. A possible remedy is to take advantage of glosses or translation in a foreign, well-resourced, language, which often exist for such data. In this paper, we explore and compare ways to exploit neural machine translation models to perform unsupervised boundary detection with bilingual information, notably introducing a new loss function for jointly learning alignment and segmentation. We experiment with an actual under-resourced language, Mboshi, and show that these techniques can effectively control the output segmentation length.
Jointly Learning to Align and Translate with Transformer Models
Sep 04, 2019
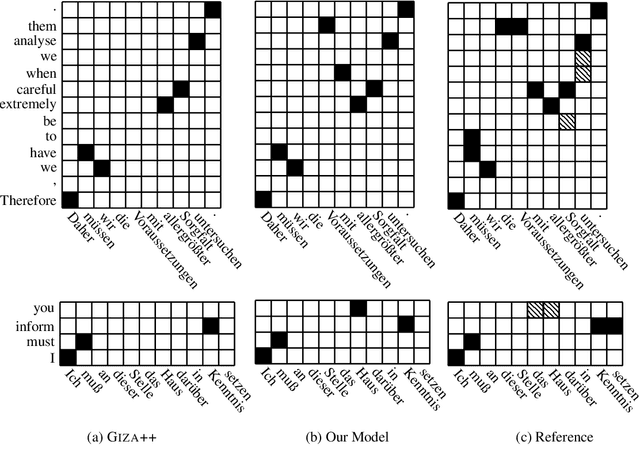
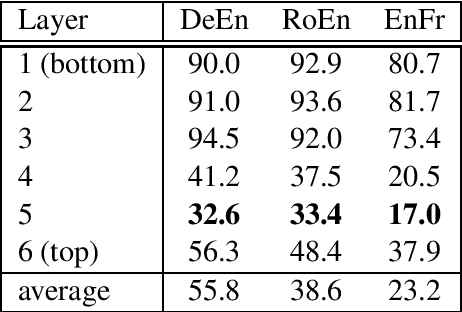
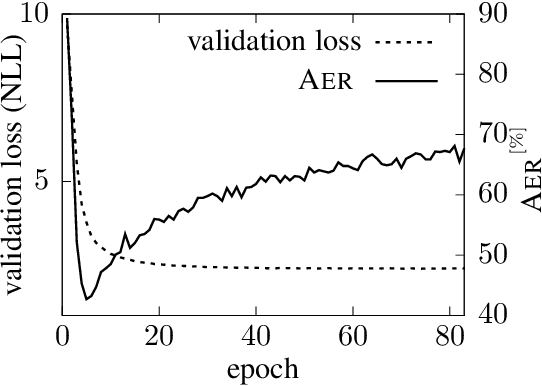
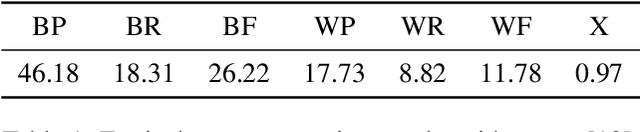
The state of the art in machine translation (MT) is governed by neural approaches, which typically provide superior translation accuracy over statistical approaches. However, on the closely related task of word alignment, traditional statistical word alignment models often remain the go-to solution. In this paper, we present an approach to train a Transformer model to produce both accurate translations and alignments. We extract discrete alignments from the attention probabilities learnt during regular neural machine translation model training and leverage them in a multi-task framework to optimize towards translation and alignment objectives. We demonstrate that our approach produces competitive results compared to GIZA++ trained IBM alignment models without sacrificing translation accuracy and outperforms previous attempts on Transformer model based word alignment. Finally, by incorporating IBM model alignments into our multi-task training, we report significantly better alignment accuracies compared to GIZA++ on three publicly available data sets.
Complete Multilingual Neural Machine Translation
Oct 20, 2020



Multilingual Neural Machine Translation (MNMT) models are commonly trained on a joint set of bilingual corpora which is acutely English-centric (i.e. English either as the source or target language). While direct data between two languages that are non-English is explicitly available at times, its use is not common. In this paper, we first take a step back and look at the commonly used bilingual corpora (WMT), and resurface the existence and importance of implicit structure that existed in it: multi-way alignment across examples (the same sentence in more than two languages). We set out to study the use of multi-way aligned examples to enrich the original English-centric parallel corpora. We reintroduce this direct parallel data from multi-way aligned corpora between all source and target languages. By doing so, the English-centric graph expands into a complete graph, every language pair being connected. We call MNMT with such connectivity pattern complete Multilingual Neural Machine Translation (cMNMT) and demonstrate its utility and efficacy with a series of experiments and analysis. In combination with a novel training data sampling strategy that is conditioned on the target language only, cMNMT yields competitive translation quality for all language pairs. We further study the size effect of multi-way aligned data, its transfer learning capabilities and how it eases adding a new language in MNMT. Finally, we stress test cMNMT at scale and demonstrate that we can train a cMNMT model with up to 111*112=12,432 language pairs that provides competitive translation quality for all language pairs.
Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate
May 19, 2016



Neural machine translation is a recently proposed approach to machine translation. Unlike the traditional statistical machine translation, the neural machine translation aims at building a single neural network that can be jointly tuned to maximize the translation performance. The models proposed recently for neural machine translation often belong to a family of encoder-decoders and consists of an encoder that encodes a source sentence into a fixed-length vector from which a decoder generates a translation. In this paper, we conjecture that the use of a fixed-length vector is a bottleneck in improving the performance of this basic encoder-decoder architecture, and propose to extend this by allowing a model to automatically (soft-)search for parts of a source sentence that are relevant to predicting a target word, without having to form these parts as a hard segment explicitly. With this new approach, we achieve a translation performance comparable to the existing state-of-the-art phrase-based system on the task of English-to-French translation. Furthermore, qualitative analysis reveals that the (soft-)alignments found by the model agree well with our intuition.
Deep learning based unsupervised concept unification in the embedding space
Jun 05, 2019



Humans are able to conceive physical reality by jointly learning different facets thereof. To every pair of notions related to a perceived reality may correspond a mutual relation, which is a notion on its own, but one-level higher. Thus, we may have a description of perceived reality on at least two levels and the translation map between them is in general, due to their different content corpus, one-to-many. Following success of the unsupervised neural machine translation models, which are essentially one-to-one mappings trained separately on monolingual corpora, we examine further capabilities of unsupervised deep learning methods used there and apply these methods to sets of notions of different level and measure. Using the graph and word embedding-like techniques, we build one-to-many map without parallel data in order to establish a unified latent mental representation of the outer world, by combining notions of different kind into a unique conceptual framework. Due to latent similarity, by aligning two embedding spaces in purely unsupervised way, one obtains a geometric relation between objects of cognition on the two levels, making it possible to express a natural knowledge using one description in the context of the other.
Modeling Coverage for Neural Machine Translation
Aug 06, 2016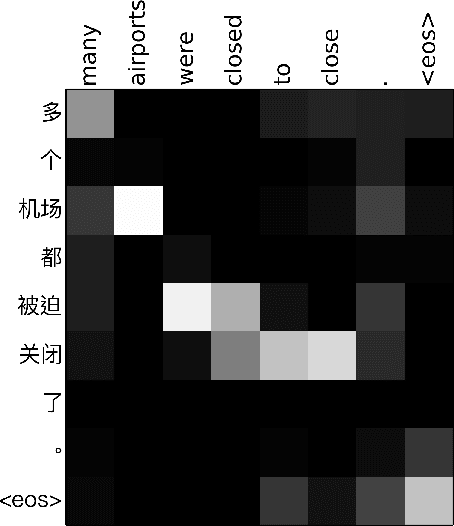

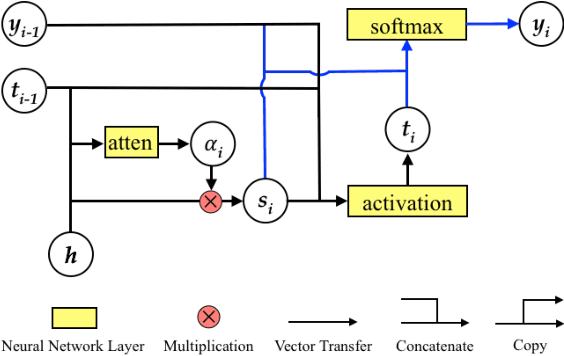
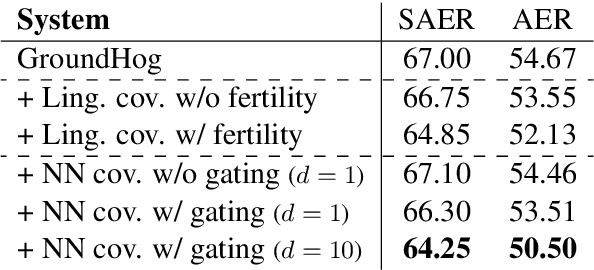
Attention mechanism has enhanced state-of-the-art Neural Machine Translation (NMT) by jointly learning to align and translate. It tends to ignore past alignment information, however, which often leads to over-translation and under-translation. To address this problem, we propose coverage-based NMT in this paper. We maintain a coverage vector to keep track of the attention history. The coverage vector is fed to the attention model to help adjust future attention, which lets NMT system to consider more about untranslated source words. Experiments show that the proposed approach significantly improves both translation quality and alignment quality over standard attention-based NMT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge